Frequently asked questions about the high-rise multifamily solar photovoltaic (PV) requirements for the 2025 Energy Code.
General Information
Section 170.2(g) - PDF of the 2025 Energy Code requires solar photovoltaic (PV) systems for all newly constructed high-rise multifamily buildings (buildings that have four or more habitable stories), with five exceptions (see below).
These requirements apply to buildings where at least 80 percent of the total floor area (conditioned or not) serves one or more of building types specified in Table 170.2-U - PDF, including mixed-occupancy buildings.
These building types include:
- Events & exhibits
- High-rise multifamily
- Hotel/motel
- Library
- Office, financial institution, unleased tenant space, medical office building/clinic
- Restaurants
- Retail, grocery
- Religious worship
- Sports & recreation
- School
- Warehouse
These requirements do not apply to additions or alterations to existing buildings.
The required solar PV size is calculated per Section 170.2(g) - PDF. A building’s energy demand is impacted by its climate zone (CZ), conditioned floor area (CFA), and space usage. The minimum required solar PV system is intended to approximately offset the annual electrical consumption of the proposed building, as if it were a mixed fuel building such that it will self-utilize about 80 percent of the solar PV generation without a battery energy storage system (BESS), and about 90 percent with a battery energy storage system (BESS).
Prescriptive Requirements
Section 170.2(g) - PDF of the 2025 Energy Code outlines two methods to determine the minimum solar PV system size. The required size is the smaller of either the capacity based on solar access roof area (SARA) or based on Equation 170.2-D:
- Solar access roof area (SARA):
- Steep-sloped roofs: SARA multiplied by 18 watts per square foot
- Low-sloped roofs: SARA multiplied by 14 watts per square foot
- Equation 170.2-D considers three factors:
- Building type
- Climate zone (CZ) of the building
- Conditioned floor area (CFA) of the building
Solar access roof area (SARA) includes roof areas, covered parking, carports, and newly constructed structures on the property that can support a solar PV system per Title 24, Part 2, Section 1511.10. SARA excludes roof areas:
- With less than 70 percent annual solar access accounting for shading from all obstructions
- Occupied as specified by California Building Code Section 503.1.4
- Roof area otherwise unavailable due to compliance with:
- Other state building code requirements
- Local building code requirements if confirmed by the California Energy Commission Executive Director
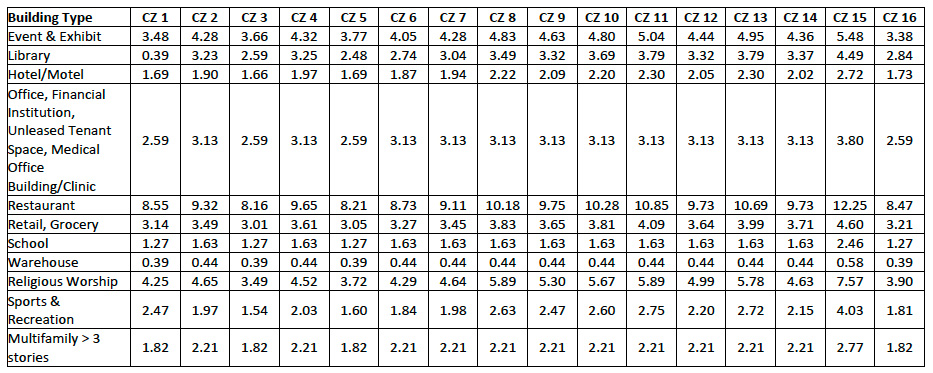
For mixed occupancy buildings, minimum rated PV system capacity is calculated by applying Equation 170.2-D to the conditioned floor area of each building type listed in Table 170.2-U -PDF, and then summing the individual PV capacities for each type.
Table 170.2-U – PV Capacity Factors (Watts per square foot of condition floor area)
All high-rise multifamily buildings with solar PV systems are required to have a battery energy storage system (BESS) unless they meet an exception. For more on the requirements for battery energy storage systems, please visit the 2025 High-Rise Multifamily Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) Fact Sheet.
Performance Compliance
A building complies if the energy consumption calculated for the proposed design building is no greater than the energy budgets calculated for the standard design building, which is defined by the mandatory and prescriptive requirements. Increasing building energy efficiency can reduce the required solar PV system size.
Yes. There are five exceptions that exclude high-rise multifamily buildings from the solar PV requirements
- Total SARA is less than 3 percent of the conditioned floor area
- Minimum required solar PV system capacity is less than 4 kWdc
- SARA is less than 80 contiguous square feet
- The enforcement authority determines the solar PV system cannot meet the American Society of Civil Engineers Standard 7-16, Chapter 7, Snow Loads requirements
- Multitenant buildings where the load-serving entity does not offer compensation for PV generation through virtual energy bill credits.
- Exception does not apply to either:
- CEC-approved community solar program per §10-115
- Load-serving entity program that compensates PV generation through virtual energy bill credits for occupants of nonresidential and hotel/motel tenant spaces from netting of energy generation and consumption
- Exception does not apply to either:
No. Solar PV systems can be installed on the building’s SARA, ground-mounted on the property, or mounted atop a carport installed on the lot. Note: an alternative to installing solar PV on-site is to comply with community solar requirements when using the performance compliance approach if the CEC has approved a community solar program for the building type in the area where the building is located.
The solar-ready requirements under Section 110.10(b)-(d) - PDF are mandatory, but only apply to:
- Newly constructed high-rise multifamily buildings with ten habitable stories or less, that do not require a solar PV system.
- Additions where the total roof area is increased by more than 2,000 square feet (see Exception to Section 180.1(a)1 - PDF)
For information on low-rise multifamily buildings, please visit the 2025 Low-rise Multifamily Solar PV Factsheet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. The prescriptive requirements in Section 170.2(f-g) for PV apply to new multifamily buildings. The battery energy storage systems requirements in Section 170.2(h) - PDF apply to new multifamily buildings with more than three habitable stories.
No. The prescriptive requirements for PV and battery energy storage systems only apply to newly constructed buildings.
No. The PV and BESS capacity factors apply separately to each corresponding building type. For example, if 85 percent of a building is high-rise multifamily, the multifamily capacity factor applies to 85 percent of the building. If 15 percent is office space, the office capacity factor applies to the other 15 percent of the building.
Yes. For mixed use low-rise buildings, the PV and BESS requirements for non-residential or hotel/motel building types apply only if those types fall under one or more categories listed in Table 170.2-U-PDF, and the sum of those categories constitutes at least 80 percent of the total floor area. For example, if a mixed-use building consists of 21 percent low-rise multifamily building type and the remaining 79 percent of the building falls under building categories listed in Table 170.2-U-PDF, the PV and BESS requirements for non-residential or hotel/motel building types will not be triggered. However, Section 170.2(f)-PDF will still apply to the low-rise multifamily portion of the building.
Yes. Since the dining area is part of the living facility, the entire building is considered multifamily. The dining area would only be considered a restaurant if it is designed to serve outside customers. Depending on the number of habitable stories, the PV requirements in the 2025 Energy Code Sections 170.2(f-g) will apply to the entire building.
See the Blueprint for more information, including articles and frequently asked solar PV questions about the 2025 Energy Code.